Table of Contents

Are you a seafood lover? Or a health enthusiast looking to boost your nutrient intake?
If so, you‘ll want to read this blog post about the nutrition data of shrimp!
We‘ll explore the macronutrients, micronutrients, and health benefits shrimp can provide.
Plus, we‘ll discuss the potential drawbacks of consuming shrimp.
Get the facts you need to decide if shrimp is the right food for you!
Let’s say you were reading something and all of a sudden the word “seafood” appears, talking about visual effects, that word would create many images in your mind: Tuna, Salmon, crab and most definitely shrimps!
Shrimps are one of the most famous seafood.
Even people who are not fond of seafood usually like shrimp!
Here are some general facts about shrimp to start with:
General facts about shrimp:
History of shrimp:

Decapod crustacean ( have five pairs of legs ), with a long fan-shaped tail, long antennas, semi-transparent in color, the shrimp counts about 2000 species, varying in size from few centimeters to over 7 inches! (1)
The most consumed ones are grey, white, black, and tiger shrimps.
Found in every ocean around the world, both in deep water and near coasts, as well as in lakes ad freshwater streams, it feeds on small marine plants and animals.
Judging by discoveries made by French archaeologists, human beings have been consuming prawns and shellfish for at least 165,000 years! (2)
Though, it was during the period going from 17,000 BC to 7000 BC that marine products became one of human’s essential food.
It was during those times when various populations around the world learned to exploit this resource.
Shrimp facts:
How many shrimps are in a pound?

This question is so general that makes it really difficult to answer! As mentioned above, shrimps vary in size and weight, they can go from few grams to over 300 grams.
This really depends on the type of shrimp. King prawn shrimps grow up to 100 grams, so 8 King prawns are almost 1 pound!
The tiger shrimp is a bit smaller than the King prawn, they can reach about 40 grams which means a pound would be 15 to 20 tiger shrimps.
Whiteleg shrimps, on the other hand, grow up to 30 grams, and though 1 pound contains between 15 and 20 shrimp. (3)
As for most commonly consumed shrimps, small and medium sizes, 1 pound should be between 20 and 40 shrimps!
Are shrimps bugs?

Think of it for a second, people who eat shrimps are eating the equivalent versions of roaches, pretty disturbing right?!
Although, when it comes to tasty food, people would only consider what they have in hand without bothering to know such details.
Before moving to the scientific facts, shrimps are obviously the aquatic versions of what we know as bugs! Does that mean that shrimps are bugs?
Shrimps are crustaceans and those are not bugs, but they are closely related to them.
Bugs (or insects) and crustaceans are classified as Arthropods, so they are by definition sisters in the same phylum. (4)
A very recent DNA research suggests that insects could have evolved from crustaceans, which makes insects an evolved type of shrimp. (5)
That means that shrimps are not yet bugs, they could be, maybe in a million years so you should not worry about your purchased shrimp turning to bugs after you get them!
How much shrimp per person?

There is no specific number, as we always have the same issue: shrimps differ so much in size and weight!
We can tackle that issue by thinking of the amount of protein we aim for, so it depends on the meal.
Here are some factors that could help knowing how much shrimp per person:
- 1 cup/8oz of raw shrimp per person for a main dish.
- ½ cup/4oz of raw shrimp per person for an appetizer.
Shrimp lose up to 30% of weight after getting peeled and cooked, so 1 cup of raw shrimp will be 6 ounces of cooked shrimp meat! And that is the perfect amount for the main dish.
Most people like eating cold shrimp.
Evenly cooked shrimp can last up to 5 days in the refrigerator, just make sure you put them under refrigeration within 2 hours of cooking!
Shrimp grill time:

Shrimp get overcooked very easily, you have to watch them as they cook to avoid wasting them.
Don’t worry though, it won’t be long-standing! Like most seafood, shrimp take about 2 to 3 minutes per side to be grilled evenly and properly!
It’s so easy to tell when shrimp are properly cooked as they turn pink and darker.
Another tip when cooking shrimp is to take them off when they are barely cooked, even if they are still raw in the middle.
The heat of the shrimp will continue cooking its inside after you pull them off!
Shrimp nutrition data:
These data are provided by the USDA for ½ cup of cooked or boiled shrimp (4 ounces, 10-12 shrimp): (6)
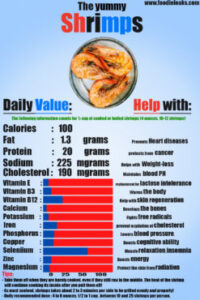
- Calories: 100
- Fat: 1.3g
- Protein: 21g
- Sodium: 111mg
- Cholesterol: 190mg
- Fiber: 0g
- Sugars: 0g
- E vitamin: 8%
- B3 vitamin: 12%
- B12 vitamin: 28%
- Calcium : 5%
- Potassium : 8%
- Iron: 20%
- Phosphorus: 16%
- Copper: 15%
- Selenium: 64%.
- Zinc: 12%
- Magnesium: 9%
Shrimp is the most consumed type of seafood across the globe thanks to its delicious flavor.
The inside of a shrimp is full of white lean meat with a very low-calorie proportion and fat.
The size of shrimp varies from 2in for the small types to 9in the case of royal red shrimp and farmed shrimp-like whiteleg.
In terms of shrimp nutrition data, these prawns have a lot to offer as they are a great asset to our health.
The abundance of vitamins and minerals shrimp offers gives them their good reputation in offering many health benefits.
Among the most abundant nutrients in shrimp, it contains phosphorus, copper, iron, zinc, magnesium, selenium, and a high proportion of vitamin B12 and vitamin E, and a small content of vitamin C and vitamin A.
A good source of protein:
Among the best sources of protein, we find meat, seeds, and seafood and shrimp are not an exception.
The unique thing about shrimp protein is that it contains 20 amino acids including all the 9 essential ones our bodies need. (7)
The body uses those amino acids to produce digestive enzymes, hormones, regenerate the skin, and maintain muscle mass…
Contains carotenoids and Q10:
There are different types of shrimp but most of the types have red or orange color shades.
These colors are due to the Astaxanthin content of the carotenoids family, which is the same coloring pigment in carrots. (8)
This pigment has incredible antioxidant properties that are even stronger than that of vitamin E and beta-carotene.
In fact, astaxanthin in shrimp may protect against cancer, chronic and cardiovascular diseases.
In addition, shrimp contains CoQ10 and which is a type of coenzyme that acts as a vitamin and is similar to vitamin K.
Some studies show that CoQ10 prevents cardiovascular diseases and reduces blood pressure which is beneficial for hypertensive people. (9)
Also, CoQ10 in shrimp prevents the oxidation of bad cholesterol LDL which guarantees a better blood flow.
Contains Omega-3 fatty acids:
Other beneficial nutrients in shrimp are omega-3 fatty acids, specifically EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) fatty acids. (10)
These types of fatty acids are most abundant in some plants and seafood including salmon, tuna, and shrimp.
Researches suggest that EPA and DHA contribute to the well-being of our cardiovascular health and lowers the fatality rate of heart diseases. (11)
A great source of magnesium:
Now we all know that seafood is a great source of minerals and one of them is magnesium.
In fact, the recommended dose of shrimp of ½ cup (10 to 12 shrimp) offers around 10% of the daily need in magnesium.
This mineral is essential for bone development, dental health, immune system functioning, and muscle contraction.
Also, magnesium plays a key role in the transmission of nerve impulses and the overall energy metabolism in our bodies. (12)
Shrimp offers selenium:
Selenium is among the most powerful antioxidants that we can good from our food such as shrimp.
As a matter of fact, the daily serving of shrimp offers about 60% of our daily needs in selenium. (13)
This mineral acts as an enzyme and prevents the formation of free radicals in the body which are the source of most diseases.
Also, it helps convert thyroid hormones into their active form to keep the body warm and maintain cognitive health.
Offers phosphorus:
Now when we talk about bone and tooth health, most people think about calcium and forget the role of phosphorus.
Phosphorus is almost on the same level of importance when it comes to bones and teeth formation as many studies suggest. (14)
In addition, phosphorus is one of the constituents of cell membranes and helps the body create ATP, a molecule that stores energy.
It also participates in the regeneration of body tissues and maintains a stable PH level in the blood.
A good source of iron:
Among the many roles of iron, it helps transport the oxygen from the blood to the cells, mostly muscle cells.
Iron is an essential element in the production of red blood cells as well as in the production of neurotransmitters and hormones.
A serving of shrimp offers about 20% of our daily need in iron and that is a good boost to our need for this nutrient.
Shrimp offers copper:
These sea prawns are so abundant in copper and offer more than 30% of our daily need of copper per one serving. (15)
Copper is among the very essential nutrients our bodies need for many functions including:
- Fighting free radicals.
- Creates hemoglobin (red blood cells).
- Converts sugar to energy.
- Maintains nerve cells
- Promote bones health.
- Formation of collagen (essential to repair damaged cells).
A great source of zinc:
As most seafood are full of beneficial and essential minerals, shrimp are also a great source of zinc with 20% of our daily need in one serving.
Zinc is involved in the production of our genetic material, wound healing, and fetal development during pregnancy.
Some researches also prove the effectiveness of zinc in the quantity and quality production of sperm for men. (16)
Also, zinc is among the nutrients our body needs to smell and taste food as well as store and release insulin.
Vitamin E in shrimp:
With 10% of our daily need in vitamin E per serving, shrimp can give our bodies a better antioxidant potential.
In fact, vitamin E is a major antioxidant and it offers a lot of support to our immunity system by protecting cell membranes.
In addition, it can help in case of internal and external inflammation as it promotes healthier skin and ensures a natural blood flow.
Shrimp are full of vitamin B12:
This vitamin is sometimes called cobalamin, and it is very abundant in shrimp with more than 20% of our daily need per serving.
Among the many health benefits of the B12 vitamin it helps: (17)
- Creates DNA and genetic material.
- Prevent anemia.
- Maintain blood and neurotransmitters healthy.
- Metabolize certain amino acids.
Calories in one shrimp:

Shrimp have a reasonable amount of calories: with 94 calories for 1 cup of shrimp, they are less caloric than duck meat, chicken meat, or pork.
One shrimp is almost 8 calories.
Are the calories high in shrimp?

Shrimp are praised for their low-calorie intake if we compare it to the overall calorie intake we need per day.
Also, shrimp contain no carbohydrates, and a major part of their calories come from their protein content.
However, the calories of shrimp depend on the way you prepare them which is why we gathered this data to give you a better idea.
It is the addition of several other substances that may increase the overall calorie value of a shrimp dish.
These are the calorie value of some famous shrimp recipes per 3.5oz (100g):
- Shrimp salad: 198 calories.
- Cooked shrimp (boiled): 99 calories.
- Noodle with shrimp: 346 calories.
- Soup with cream and shrimp: 61 calories.
- Grilled shrimp: 259 calories.
Are shrimp high in cholesterol?

Yes, they are! The question should be: which cholesterol does shrimp have? Yep, there are different types of cholesterol!
In fact, your body creates cholesterol more than anything you could ever eat.
In almost all the data about seafood, shrimp are among the highest when it comes to cholesterol.
That’s because their cellular membrane is made of cholesterol.
Although they are high in cholesterol, they are low in saturated fat.
They do not raise the cholesterol level in the body.
However, avoid fried food in general and you should be good to go!
Consuming shrimp nutrition data:

You can eat shrimp raw or cooked lightly however, it is better to avoid consuming them raw and cooked them in a recipe instead.
The meat of a shrimp is very fragile and doesn’t require extensive cooking as they only need 3 minutes to be boiled.
Also, you can cook shrimp in steam which will preserve most of their nutrients.
Some people like to grill their shrimp or pan-fry them and this is the would risk losing a lot of shrimp nutrition but we can’t deny that fried or grilled shrimp is so delicious.
There are many shrimp recipes you can use to widen your shrimp menu and enjoy trying different ideas including:
- Fried shrimp with herbs and garlic.
- Boiled shrimp.
- Shrimp in the sauce.
- Avocado cocktail with shrimp (boiled and blended).
- Spring rolls with shrimp and chicken.
- Shrimp salad.
- Grilled shrimp skewers.
- Shrimp fritters.
- Creamy tagliatelle with shrimp. (18)
Precautions you need to know before you consume shrimp nutrition data:

You probably heard of seafood possibly containing toxins such as mercury.
Well, this is true but it is mostly a danger in case of large consumption of shrimp with more than 5 ounces a day.
Generally, shrimp are safe for most people when consumed in moderate amounts of less than 4 ounces a day.
However, in case of overconsumption, we may risk having vision problems or fetal health issues during pregnancy.
Raw shrimp may cause poisoning:
Shrimp, just like salmon or tuna may be a favorable environment for parasites and bacteria to grow.
Vibrio is a type of bacteria in raw shrimp that may cause abdominal pain, fever, diarrhea and in some cases can lead to severe illness for people with weak immune systems. (19)
E Coli is another bacteria in raw shrimp that may cause mild symptoms and definitely needs treatment to prevent the spread of the infection. (20)
Also, raw shrimp may contain Norovirus which is a highly contagious virus that causes muscle aches, headache, and fever. (21)
Even though these bacteria are not very dangerous but people with a compromised immune system should not eat raw shrimp.
More specifically, pregnant women, the elderly, young children, and people with chronic diseases should not eat raw shrimp.
Thus, it is probably best to never consume raw shrimp and always make sure you cook them as heat destroys these bacteria.
Shrimp are not good for gout:
This is because shrimp are rich in purines, which favors the production of uric acid which may aggravate an already existing gout condition.
In fact, a rise in uric acid levels produces a crystal that gathers in the joints and causes severe pain and even swelling.
Shrimp allergy:
Those who have a seafood allergy, are more likely allergic to shrimp as well and should avoid eating it.
Usually, these people start experiencing allergic symptoms in less than an hour of eating shrimp.
Among the symptoms these people may encounter:
- Hives
- Skin rash.
- Cramps.
- Tongue swelling.
- Nausea.
- Breathing difficulties.
It should be noted that seafood allergy may develop at any stage of life and is not an allergy that you are born with.
In the US, only 2.3% of people are allergic to seafood according to the National Institute of Health. (21)
Storing shrimp:

When you are buying fresh raw shrimp, make sure that they have not been thawed before as that tends to lower their lifespan.
Fresh and raw shrimp can be kept in the refrigerator for 3 days in an airtight container.
The reason to avoid air contact with raw shrimp is to avoid them going rancid and maybe even risk the contamination of your refrigerator.
Cooked shrimp tend to have a longer lifespan of up to 5 days in the refrigerator.
In case you want to freeze your shrimp, you can extend their lifespan to over 4 weeks.
However, make sure you use them only 2 hours after thawing them in the refrigerator and not refreeze them afterward in case you have leftovers.
Raw shrimp may be a favorable environment for bacteria growth because cooked shrimp can stay frozen for 3 to 5 months.
Buying shrimp:

The first criteria that distinguish shrimp are their freshness and you need to choose fresh shrimp when you are buying them.
Usually, fresh shrimp tend to have a firm body and a very gentle sea smell.
On the other hand, you should reject slimy shrimp or the ones that have a very pronounced unpleasant smell.
Also, rancid or old shrimp do not stick to their shell and sometimes have black spots and those are indicators of bad quality.
In case you are buying frozen shrimp, they must not be dried or frosted and most definitely not thawed before freezing them.
References:
(1): decapod | crustacean | Britannica
(2): Earliest Known Seafood Dinner Discovered – Scientific American
(3): Whiteleg Shrimp Characteristics, Feeding, Breeding (roysfarm.com)
(4): The brains of shrimps and insects are more alike than we thought — ScienceDaily
(5): An insect-like mushroom body in a crustacean brain | eLife (elifesciences.org)
(6): FoodData Central (usda.gov)
(7): Microsoft Word – 13Foxaminoacidrequirements,Foxetal.,revised.doc (uanl.mx)
(8): New Research on Astaxanthin and Cancer – – Life Extension
(9): Coenzyme Q10: The essential nutrient (nih.gov)
(10): Nutrition Facts | American Shrimp Processors’ Association
(11): FDA Announces New Qualified Health Claims for EPA and DHA Omega-3 Consumption and the Risk of Hypertension and Coronary Heart Disease | FDA
(12): The Role of Magnesium in Neurological Disorders (nih.gov)
(13): FoodData Central (usda.gov)
(14): Phosphorus – Health Professional Fact Sheet (nih.gov)
(15): Copper – Health Professional Fact Sheet (nih.gov)
(16): Zinc is an Essential Element for Male Fertility: A Review of Zn Roles in Men’s Health, Germination, Sperm Quality, and Fertilization (nih.gov)
(17): Vitamin B12 – Health Professional Fact Sheet (nih.gov)
(18): Creamy Shrimp Pasta Recipe (VIDEO) – NatashasKitchen.com
(19): Vibriosis | biomin.net
(20): Detection of pathogenic Escherichia coli and microbiological quality of chilled shrimp sold in street markets – PubMed (nih.gov)
(21):Prevalence of seafood allergy in the United States determined by a random telephone survey – PubMed (nih.gov)
