Table of Contents

Quinoa goes by the scientific name “Chenopodium Quinoa” and it is a very delicious and nutritious edible seed. (1)
It is very common in South America, especially in Ecuador, Chile, Peru, and Bolivia.
For instance, quinoa comes in different colors including red, black, or ivory, and is naturally covered with a chemical substance called Saponins. (2)
This compound protects the seeds from insects and once eaten, it has a bitter taste which is why the seeds go through a process to wash off Saponins.
However, quinoa has many important nutritional benefits and comes in the form of grains which allows it to replace rice or couscous.
In this article, we mentioned everything you need to know about quinoa seeds.
Stay tuned till the end to find our beneficial tips on how to buy quinoa seeds, how to store them, and several possible recipes you can try at home!
What are quinoa seeds?

Barley and wheat are the most famous cereals but some other seeds like quinoa are similar to cereals and we may hear about for the first time.
This could be because these exotic seeds are limited or only available in some countries.
Originated in South America, quinoa is an edible seed related to other plants such as beets and spinach.
Quinoa leaves are also edible and used in many dishes in South American cuisines mainly as a nutritive and flavorful vegetable. (3)
Quinoa seeds now and back then:

The origin of this super-seed dates back to ancient times with ancient civilizations such as the Andean.
In fact, it was the main source of nutrition for the people of that region for more than 6,000 years. (4)
Andeans called it Quechua in their local dialect and throughout the time with the effect of more Latin dialects inhabiting the region it changed to “Quinoa”.
For instance, it was long believed that Native Americans got their energy and power from quinoa which helped them fight against colonization.
It was for that same reason, cultivation of quinoa seeds was prohibited and there was several penalties for those who violate the rules.
Consequently, this led to the disappearance of quinoa plantations in the region for a long time.
Several years after in the 80s to be exact, quinoa cultivation started to thrive again. (5)
Presently, other regions started growing quinoa plants especially in the eastern regions of North America.
Nowadays, the USA is the 4th large producer worldwide after Bolivia and Peru which combined account for more than 90% of the global production.
Quinoa seed AKA superpower seeds:

The quinoa plant is rich in many nutrients such as minerals, vitamins, and plant-based compounds.
Many believe that quinoa is the mother of all grains because it contains all types of amino acids and that makes it a complete source of vegetarian protein.
It is true that plant-based proteins are slightly harder to digest compared to meat protein but they still offer a great protein option for vegetarians and vegans. (6)
Therefore, quinoa seeds are by far the best choice for a healthy vegan lifestyle because they provide a complete and better substitute for meat protein.
In addition to that, it is also the best and probably the most suitable option for people with a gluten allergy since these seeds are gluten-free.
Another group of people who can use quinoa seeds as a substitute is people with a lactose intolerance since these grains offer a good amount of calcium.
Also, they offer a good amount of dietary fibers necessary for the well-being of our digestive system.
Quinoa seeds are also full of many minerals such as magnesium, phosphorus, manganese, zinc…
Hence, calling quinoa seeds “superpower seeds” is actually pretty accurate as it provides almost a complete source of food by itself!
Quinoa seeds nutrition:
The following information counts for 100g (almost 1/2cup) of cooked quinoa seeds: (7)
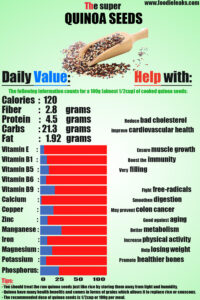
- Calories: 120
- Protein: 4.5g
- Carbs: 21.3g
- Sugar: 0.87g
- Dietary fibers: 2.8g
- Fats: 1.92g
- E vitamin: 6%
- B1 vitamin : 10%
- B5 vitamin : 13%
- B6 vitamin : 9%
- B9 vitamin: 22%
- Calcium : 2%
- Copper: 20%
- Zinc: 11%
- Manganese: 32%
- Iron : 10.5%
- Magnesium : 18%
- Potassium: 9%
- Phosphorus: 28%
The health benefits of quinoa seeds result from their abundance in many essential nutrients among which we mention:
Dietary fibers:
Generally, dietary fiber consumption improves overall digestion by smoothing the transport of food through the intestines.
Once making it to the stomach, the fibers get in contact with stomach liquids then turn into a gel form and stick on the walls of the intestines.
This process reduces the infiltration of bad cholesterol through the intestines.
Furthermore, consuming more quinoa seeds will provide your body with the daily need for fiber which helps the development of beneficial bacteria. (8)
These good bacteria may reduce the risk of stomach diseases including colon cancer.
Quinoa seeds provide 2.8g of dietary fibers for every 100g and that’s 12% of the daily need in fibers.
Also, quinoa seeds are like chia or sesame seeds, they can absorb a large quantity of water and this increases their size and results in feeling full for a longer time.
Plant-based proteins:
For all the vegan “lifestylers” and even meat-eaters, quinoa offers a good amount of protein.
Unlike most sources of protein, the proteins found in quinoa are full of amino acids.
Those amino acids are essential for immunity, muscle growth, and many important body functions.
Moreover, 100g of quinoa seeds, which is ½ a cup, provides 4.5g of protein which is almost 10% of the daily need for protein.
Unlike other types of seeds, quinoa seeds protein is an excellent source of lysine. (9)
This essential amino acid plays a key role in the body’s ability to absorb protein.
Even though it’s rare, it should also be noted that a deficiency in lysine could cause serious medical problems. (10)
Minerals:
Quinoa seeds are full of many minerals essential for good health.
Among those minerals we mention:
Iron:
Any living being needs iron to support many body functions and quinoa offers a good amount of it. (11)
Some would even say it’s as essential as water!
Even though that may seem pretty exaggerating, iron is essential for many metabolic functions including the transportation of neurons and oxygen.
Calcium:
Mostly linked to milk, this mineral exists abundantly in quinoa seeds as well.
Calcium plays a key role in several body functions including neuro-transmission and the formation of tissues in our flesh and bones.
Zinc:
Just like calcium and iron, zinc is among the essential minerals that our body needs to function.
It is necessary for the process of manufacturing and breaking down fats, proteins and carbohydrates.
The amount of zinc in quinoa is 2 times that of chiaseeds or flaxseeds. (12)
Other minerals:
Those were the most abundant ones but in addition, quinoa contains other minerals in small quantities including phosphorus, magnesium, and potassium.
Plant components:
Quinoa seeds are a good source for many plant compounds responsible for their flavor and health benefits.
Some of the plant compounds in quinoa seeds are:
Kaempferol: (13)
An antioxidant component that can reduce the risk of cancer.
Quercetin: (14)
A polyphenol antioxidant that helps our bodies fight free radicals and as a result reduces heart disease, cancer, and osteoporosis.
Squalene: (15)
An organic component with good antioxidant properties.
It can also balance the overall oil production in the body which means clearer skin, healthier scalp, and more anti-aging abilities.
Gluten-free:
In a 2013 survey, more than 30% of people in the US are limiting their gluten consumption. (16)
This is because a gluten-free diet is super healthy as long as the products are naturally gluten-free.
So many health issues are involved with artificially gluten-free food that involves refined starch.
These artificially treated food are no better than their gluten products counterparts as junk food would still be junk after starch refinement.
So many researches were made on quinoa as a naturally gluten-free ingredient especially for those who don’t want to give up pasta or bread. (17)
These studies show that quinoa seeds are a better replacement for rice flour, potatoes, or corn as they have a better nutritional and antioxidant value.
Quinoa seeds cooking tips:

As mentioned above, raw quinoa seeds need to be soaked for 30 minutes before use in order to wash off Saponins coating.
You can also do that by boiling quinoa seeds for 20 minutes in salted water as that will ensure there are no traces of Saponins left.
After rinsing quinoa seeds you can use them in many different recipes such as:
- With steamed or grilled vegetables.
- On the side with meats.
- Instead of couscous.
- To stuff poultry or vegetables (pepper, tomatoes, zucchini…).
- A substitute for rice in risottos.
- In stews or soups.
- Precooked quinoa seeds are really good for baking recipes such as puddings, muffins, cakes…
- Quinoa seed flakes are a healthier substitute to the classic oats and taste delicious in cooked milk.
- Quinoa powder AKA Quinoa flour can replace your classic flour and works perfectly for all your recipes of waffles, pancakes, bread…
How to buy quinoa seeds?

This is really depending on the recipe you are planning to make because you can buy:
- Pre-cooked grains.
- Quinoa seed powder to use as a substitute for flour.
- Quinoa flakes to use like oats.
- Raw quinoa seeds.
Storing quinoa seeds:

Again, this depends on the quinoa seed product you want to store, for example:
- You can store quinoa flour in the freezer or refrigerator and it will keep all its properties.
- You should treat the raw quinoa seeds just like rice by storing them in a dry place away from light and humidity.
- As for pre-cooked quinoa seeds, you should store them in the refrigerator and consume them within 3 days of opening the package just like normal oats.
Quinoa allergy:

Most seeds are safe when we consume them as food and what applies to wheat applies to quinoa.
Due to the lack of information regarding the potential dangers of consuming large quantities of quinoa, we only have notices and precautions for a certain group of people.
Among the precautions related to consuming a lot of quinoa seeds we mention:
- Quinoa contains Phytates: (18)
The existence of this compound in the body reduces the ability to absorb beneficial minerals such as iron and zinc. - Quinoa contains Saponins:
A natural coating bitter to the taste acts as a thin outer shell to the seeds.
This chemical substance can cause severe stomach irritation especially for people with a poor stomach.
This is why it is recommended to soak the seeds in water for 30 minutes and rinse them well before cooking. - Quinoa during pregnancy or breastfeeding:
Because of the lack of information concerning the consumption quinoa, it is better to stay away from it and avoid any probable complications. - Quinoa Oxalates: (19)
This same compound, which can be found in spinach or beets, can contribute to the formation of kidney stones in some cases.
However, you can avoid such harmful side effects by soaking the quinoa seeds for half an hour before cooking.
Notice:
If you ate quinoa and started experiencing an increase in heart rate, stomachache, facial swelling, or pale skin you should consult a doctor.
Do not be afraid as these symptoms are usually an allergic reaction that mostly happens in case the person has an allergy to quinoa.
Don’t forget that quinoa allergy is less common than peanut allergy which makes only 1% of people, so you’re most likely safe to eat quinoa seeds and enjoy its benefits.
References:
(1): The genome of Chenopodium quinoa | Nature
(2): Saponins from edible legumes: chemistry, processing, and health benefits – PubMed (nih.gov)
(3): Nutritional Composition of the Green Leaves of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) | Pathan | Journal of Food Research | CCSE (ccsenet.org)
(4): What is Quinoa: The Seed of the Andes Explained – SA Expeditions
(5): Frontiers | The Global Expansion of Quinoa: Trends and Limits | Plant Science (frontiersin.org)
(6): The Role of the Anabolic Properties of Plant- versus Animal-Based Protein Sources in Supporting Muscle Mass Maintenance: A Critical Review (nih.gov)
(7): FoodData Central (usda.gov)
(8): The Impact of Dietary Fiber on Gut Microbiota in Host Health and Disease – ScienceDirect
(9): Quinoa: A grain packed with lysine (veganslounge.com)
(10): Hyperlysinemia: MedlinePlus Genetics
(11): Best Vegan Sources of Iron + 10 Easy Vegan Recipes – Simply Quinoa
(12): 23 High Zinc Foods for Vegans and Vegetarians (myfooddata.com)
(13): Kaempferol: A Key Emphasis to Its Anticancer Potential (nih.gov)
(14): Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin: New Insights and Perspectives for Human Health (nih.gov)
(15): Biological and Pharmacological Activities of Squalene and Related Compounds: Potential Uses in Cosmetic Dermatology (nih.gov)
(16): 21 Gluten-Free Statistics — Should You Avoid Gluten? [2022] (dealsonhealth.net)
(17): Gastrointestinal effects of eating quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) in celiac patients – PubMed (nih.gov)
(18): Phytate in foods and significance for humans: food sources, intake, processing, bioavailability, protective role and analysis – PubMed (nih.gov)
(19): Dietary oxalate and kidney stone formation (nih.gov)
